Liminal Chess Game
By Ethan Mondri→Description
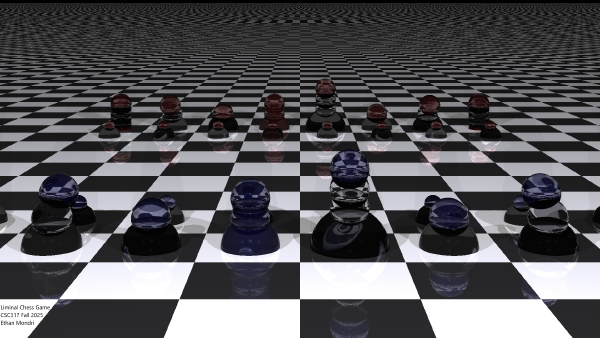
I extended the Ray Tracing assignment (A3) by implementing realistic glass refraction and procedural checkerboard textures. The scene depicts a surreal chess-like arrangement on an infinite checkerboard floor, creating a liminal space aesthetic. Using recursive ray tracing with Fresnel effects, the transparent glass “pieces” bend and reflect light in physically accurate ways. The perspective distortion of the checkerboard as it extends into the distance enhances the liminal/dreamlike quality of the scene.
Features Added
Refractive (Glass) Materials (
src/refract.cpp,include/refract.h)- Implemented Snell’s law (n₁sin(θ₁) = n₂sin(θ₂)) for realistic light refraction
- Material property
index_of_refractioncontrols how much light bends (used 1.2-1.5 in this scene) - Handles total internal reflection when light cannot escape a dense medium
- Applied to: 67 glass spheres with varying IOR values for visual variety
Fresnel Effect (
src/raycolor.cpp)- Schlick’s approximation: R(θ) = R₀ + (1-R₀)(1-cos(θ))⁵
- Angle-dependent blend between reflection and refraction for photorealistic glass
- Grazing angles become more mirror-like, direct views show more transparency
- Applied to: All 67 glass spheres compute Fresnel per-ray dynamically
Transparency System (
include/Material.h)- New
transparencyproperty (0.0=opaque to 1.0=fully transparent) - Final color blends surface shading with transmitted/reflected light
- Applied to: Glass pieces use 75-90% transparency, allowing floor to show through them
- New
Procedural Checkerboard Texture (
src/get_material_color.cpp,include/get_material_color.h)- 2D checkerboard pattern using floor(x) + floor(z) mod 2 for tile selection
- Configurable via
checkerboard_scale,checkerboard_color1,checkerboard_color2 - Only affects ambient and diffuse colors (not specular highlights)
- Applied to: Infinite ground plane with 1.0 scale black/white tiles
Enhanced Material System (
include/Material.h)- Extended Material struct with 7 new properties:
index_of_refraction(double, default 1.0)transparency(double, default 0.0)use_checkerboard(bool, default false)checkerboard_scale(double)checkerboard_color1andcheckerboard_color2(Vector3d)
- Backwards compatible via constructor defaults
- Applied to: 4 material types defined in scene JSON
- Extended Material struct with 7 new properties:
Extended JSON Parser (
include/read_json.h)- Added parsing for new material properties with optional fields
- Uses
jmat.count("property")to check existence before reading - Gracefully handles both old scenes (ignoring new properties) and new scenes
- Applied to:
glass-chessboard.jsondefines materials with full property set
Increased Recursion Depth (
main.cpp)- Ray tracing depth raised from 4 to 8 recursive calls (Necessary for light to refract through multiple stacked glass spheres)
- Each reflection/refraction decrements counter, preventing infinite loops
- Applied to: Every primary ray from camera
High Resolution Rendering (
main.cpp)- Output resolution set to 1920×1080 for high detail
- Progress indicator prints every ~8% completion
- Applied to: Final output
Acknowledgements
Base Code
- CSC317 Ray Tracing Assignment (A3)
- Original assignment framework: https://github.com/alecjacobson/computer-graphics-ray-tracing
External Libraries
- Eigen: Linear algebra library (http://eigen.tuxfamily.org)
- JSON for Modern C++: JSON parsing library by Niels Lohmann (https://github.com/nlohmann/json)
Algorithms and References
- Snell’s Law Implementation: Based on “Fundamentals of Computer Graphics” (4th Edition) by Steve Marschner and Peter Shirley, Section 13.1
- Fresnel Effect: Schlick’s approximation as described in “Fundamentals of Computer Graphics” (4th Edition) by Steve Marschner and Peter Shirley, Section 13.1
Assets
All geometry in this scene is procedurally generated (spheres and planes). No external 3D models were used. Scene JSON was hand-built.
Technical Notes
Key Implementation Details
- Refraction Direction: The
refract()function implements vector form of Snell’s law, returning false when total internal reflection occurs - Ray Offset: Secondary rays offset by ±1e-6 along surface normal to prevent floating-point self-intersection
- Material Blending: Final RGB = (1-T)·surface + T·(F·reflection + (1-F)·refraction) where T=transparency, F=Fresnel
- Checkerboard Pattern: Uses
floor()on world X,Z coordinates; even/odd sum determines tile color
Created for CSC317 Computer Graphics, Fall 2025
University of Toronto