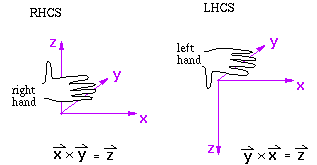Introduction to Geometric Transformations
[Hill: 209-216. Foley & van Dam: p. 201]
Translation, rotation, scaling, and shearing are all examples of geometric
transformations. Multiple copies of an object can be created by drawing
the same object using a series of different transformation matrices.
 (image courtesy of Robert Lansdale)
(image courtesy of Robert Lansdale)
The Graphics Pipeline
Most rendering algorithms can be separated into two or more distinct stages.
The graphics pipeline is a useful abstraction of the rendering process
as well as a block diagram for dedicated graphics hardware.

Definitions Related to Geometric Transformations
-
affine transformation
-
A transformation which preserves the parallelism of lines, but not necessarily
angles or lengths.
-
right-handed and left-handed coordinate systems
-
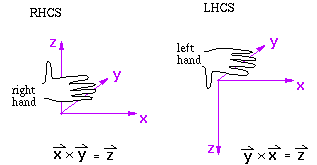
-
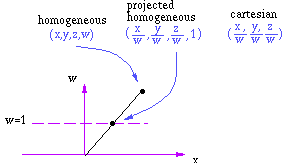
homogeneous coordinates
-
In homogeneous coordinates, each cartesian point (x,y,z) is represented
in a redundant manner by 4 coordinates, (hx,hy,hz,h). Setting w=0 can be
thought of as a point at infinity or, more simply, a direction.
-
 (image courtesy of Robert Lansdale)
(image courtesy of Robert Lansdale) (image courtesy of Robert Lansdale)
(image courtesy of Robert Lansdale)