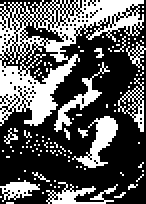Video Raster Graphics
[Hill: p. 22-29. Foley & van Dam: p. 145-184]
virtual raster device
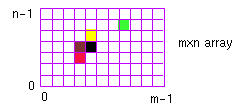
real device
video signal format
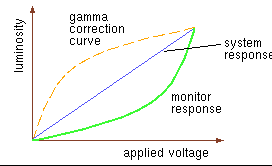
gamma correction
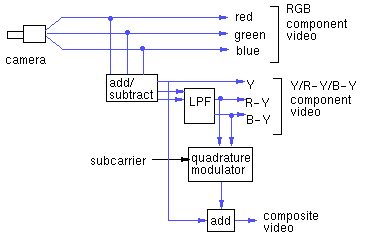
component and composite video
-
NTSC
-
North America & Japan
-
30 Hz, interlaced
-
525 lines (648 x 486)
-
PAL
-
Commonwealth & Western Europe
-
25 Hz, interlaced
-
625 lines
-
SECAM
-
France, Eastern Europe, Middle East
-
25 Hz interlaced
-
625 lines
-
HDTV
-
16:9 aspect ratio
-
digital, interlaced or progressive?
Other display devices
-
Passive Liquid Crystal
-
Active Matrix (TFT)
-
Plasma Panel
Definitions
-
Pixel aspect ratio
-
width / height: usually 1
-
Image aspect ratio
-
m/n: 4/3 for NTSC, 16/9 for HDTV
-
Refresh rate
-
NTSC: 30Hz (interlaced)
PAL, SECAM: 25Hz (interlaced)
most displays: 60 or 72Hz non-interlaced
film?
-
-
-
Phosphorescence
-
light given off after electron beam has passed
-
Critical Fusion Frequency
-
Image refresh frequency at which image appears steady (no perceptable flicker)
-
Monitor bandwidth
-
Rate at which electron beam can turn on and off
-
Spot size
-
diameter of a single dot on the output device
-
Bloom
-
phosphor excitation beyond area of electron excitement
-
Resolution
-
Density of lines that can be resolved
Basic display architecture
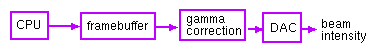
Pixels
-
bit-map: 1 bit/pixel
-
grey scale: 8 bits/pixel
-
colour map: 8 bits/pixel, indirect
-
true colour: 24 bits/pixel
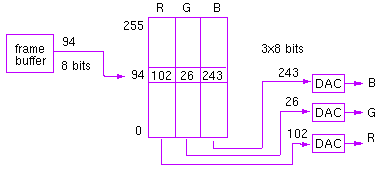
Colour maps
[Hill: 26-29. Foley & vanDam: p. 564-573, 599-600]
Colour maps are commonly employed to reduce the memory requirements
for the framebuffer. Desired RGB display colours are numbered and stored
in the corresponding row of the colour map. The framebuffer need only store
the colour numbers in this way. The compromise is that the number of simultaneously
displayable colours is limited.
What algorithms might one use to generate a colour-map?
Halftoning
Many screens and printers produce are capable of producing only black or
white. Nevertheless, one would like to be able to display approximations
of continuous-tone images on these devices. A solution is available by
relying on the spatial integration that our eyes perform.
The following image is an example of the use of dithering to
create an approximation of a continuous-tone image.

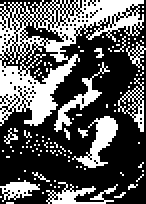
Napoleon Visual by www.PDImages.com